Children's Health
Children's Health and the Importance of PIQ Loss
About PM2.5
What is PM2.5 Air Pollution?
Which air pollutants cause diseases in children? The pollutant most to blame is PM2.5 air pollution. PM2.5 pollution is made up of tiny, invisible particulates with a diameter of less than 2.5 microns – many times smaller than the diameter of a human hair. (4)
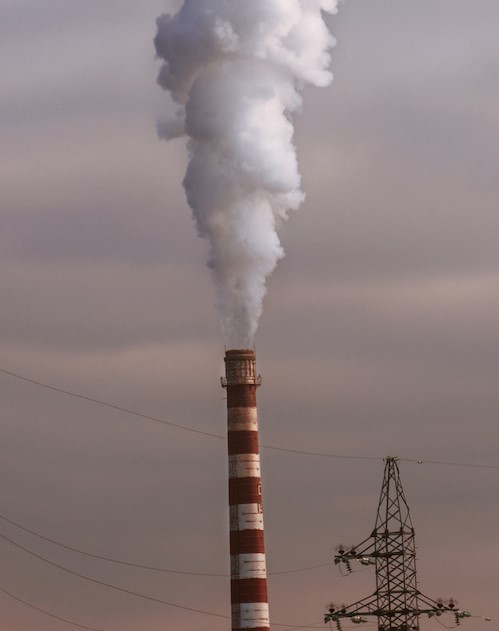

The particles in PM2.5 pollution are so small that they can penetrate deep into the lungs when they are inhaled and they can enter the bloodstream. Once they are in the bloodstream, they can reach every organ in the body to cause damage to tissues and cells (4, 5).

PM2.5 and Children
PM2.5 is harmful to people of all ages, but is especially dangerous for children. Compared to adults, children’s bodies are more susceptible to PM2.5 pollution (1, 6). Because of this, PM2.5. can cause many negative health effects in children including asthma, reduction in brain volume, behavioral dysfunction, ADHD, Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), and impaired lung growth. A mother’s exposure to PM2.5 during her pregnancy increases the risk of premature birth, low birth weight and stillbirth (7-10).
There is also growing evidence that PM2.5 pollution decreases children’s intelligence (11). Performance IQ (PIQ), the type of intelligence that enables children to solve problems and react to new situations, seems to be the form of intelligence most strongly affected by air pollution. IQ scores are highly correlated with academic performance, standardized test scores and high-school graduation rates, and thus loss of IQ caused by air pollution prevents children from attaining their full potential.
What are the Sources of PM2.5 Air Pollution?
Massachusetts sources currently emit around 2,500 tons of PM2.5 pollution each year. Most of this pollution is produced by the combustion of fossil fuels (12). Combustion of gasoline and diesel fuel in cars, trucks, and other vehicles is responsible for about 15% of PM2.5 pollution in Massachusetts. Nearly all of the rest (more than 85%) comes from stationary sources such as industrial facilities and electricity generating plants (13).